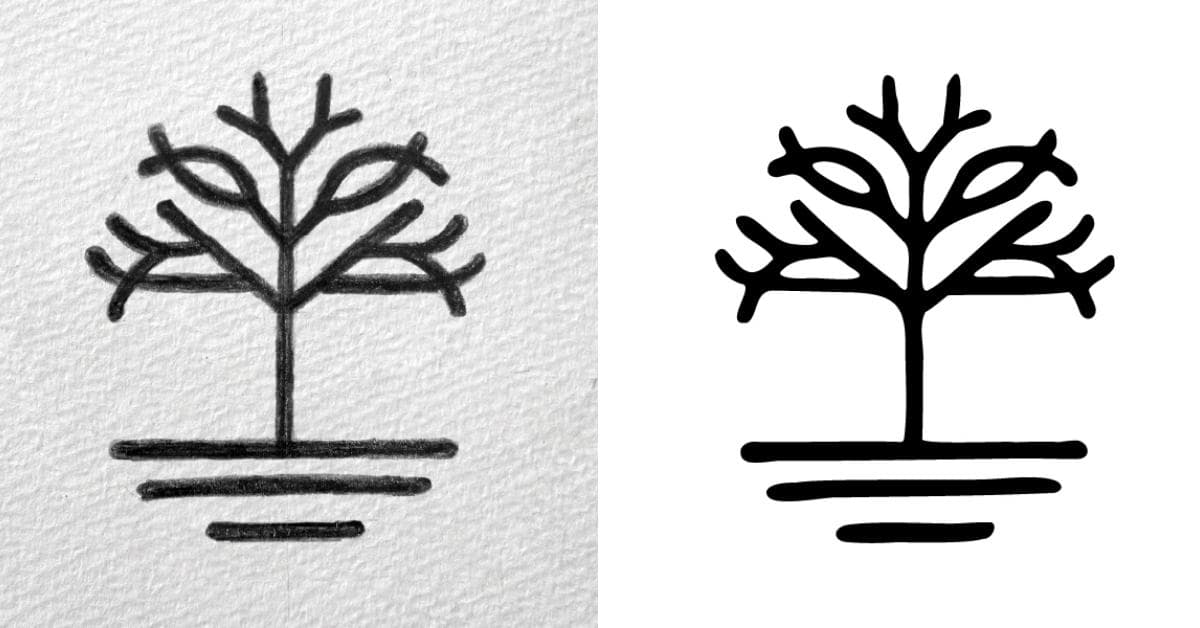
In today’s digital age, the demand for high-quality graphics and scalable images is ever-increasing. Converting hand-drawn sketches or drawings into vector format is a common requirement for various applications, such as logo design, illustration, or printing. This process can be a game-changer, allowing you to scale your artwork without any loss of quality. In this article, we’ll walk you through the steps to convert a drawing to a vector, ensuring that you have a clear understanding of the process.
What is Vectorization?
Vectorization is the process of converting a raster or bitmap image, which is made up of pixels, into a vector image, which is composed of mathematical equations that describe shapes and curves. Vector images are resolution-independent and can be scaled to any size without losing quality. They are commonly used in graphic design, logo creation, and for producing crisp, high-quality prints.
Why Convert a Drawing to Vector?
Converting a drawing to vector offers several advantages:
- Scalability: Vector images can be resized without any loss of quality, making them ideal for large banners, billboards, or small icons.
- Editing Flexibility: Vector files can be easily edited, allowing you to fine-tune your artwork, change colors, or adjust shapes.
- Smooth Lines: Vectorized drawings have smooth and clean lines, eliminating pixelation or jagged edges.
- High-Resolution Output: Vector images are perfect for producing high-quality prints and designs.
Tools and Software for Vectorization
There are various software options available for converting drawings to vectors, but the most popular ones include:
- Adobe Illustrator: A professional-grade vector graphics editor that offers a wide range of features and tools for vectorization.
- Inkscape: A free and open-source vector graphics editor that’s a great option for those on a budget.
- CorelDRAW: A comprehensive vector graphics editor, popular for professional use.
Steps to Convert a Drawing to Vector
Follow these steps to convert your drawing to vector:
- Scanning or Digital Photography: Start by digitizing your hand-drawn artwork by scanning it at a high resolution or taking a high-quality photo. Ensure good lighting and minimal shadows.
- Importing Your Image: Open your chosen vector software and import your scanned or photographed drawing.
- Tracing Your Drawing: Use the vectorization tools within your software to trace over the lines of your drawing. This can involve using the Pen Tool, Bezier curves, or other drawing tools. Be patient and take your time to ensure accuracy.
- Refining and Editing: After the initial tracing, refine your vector image. You can adjust lines, colors, and shapes as needed to achieve the desired result. Pay attention to details and make sure the image looks clean and polished.
- Saving in Vector Format: Once you’re satisfied with your vector image, save it in a vector format like .AI (Adobe Illustrator), .SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics), or .EPS (Encapsulated PostScript).
Best Practices for Vectorizing Drawings
- Use a stylus or drawing tablet for more precise control during the tracing process.
- Save your work regularly to avoid losing progress.
- Keep your vector paths organized and labeled.
- Experiment with different tools and techniques to achieve the best results.
- Always work on a copy of your original drawing to preserve the original.
FAQs
Q1: Can I vectorize a hand-drawn sketch without any design skills?
Yes, you can, but it may take some practice and patience. Many vectorization tools offer automatic tracing features that can help simplify the process for beginners.
Q2: What’s the best resolution for scanning a drawing for vectorization?
For high-quality results, scan your drawing at a minimum of 300 DPI (dots per inch) or higher.
Q3: What if my drawing has multiple colors?
You can vectorize multicolored drawings by using the software’s tools to create separate vector objects for each color. This allows for easy color adjustments and editing.
Q4: Can I convert a vector image back into a raster image?
Yes, you can export or save a vector image in raster formats like JPEG or PNG if needed, but keep in mind that this will not improve the resolution or quality of the image.
Q5: Is vectorization suitable for all types of drawings?
Vectorization is most effective for drawings with well-defined lines and shapes. Complex or highly detailed images may require more time and effort to vectorize.
In conclusion, converting a drawing to a vector image is a valuable skill for graphic designers and artists. With the right tools and software, you can create high-quality, scalable vector art that’s perfect for a wide range of applications. Whether you’re a professional designer or a hobbyist, vectorization can elevate your artwork to the next level.
This page was last edited on 22 February 2024, at 5:45 pm